Regulatory Compliance for Electronics: What You Need to Know
February 19, 2025
Table of contents
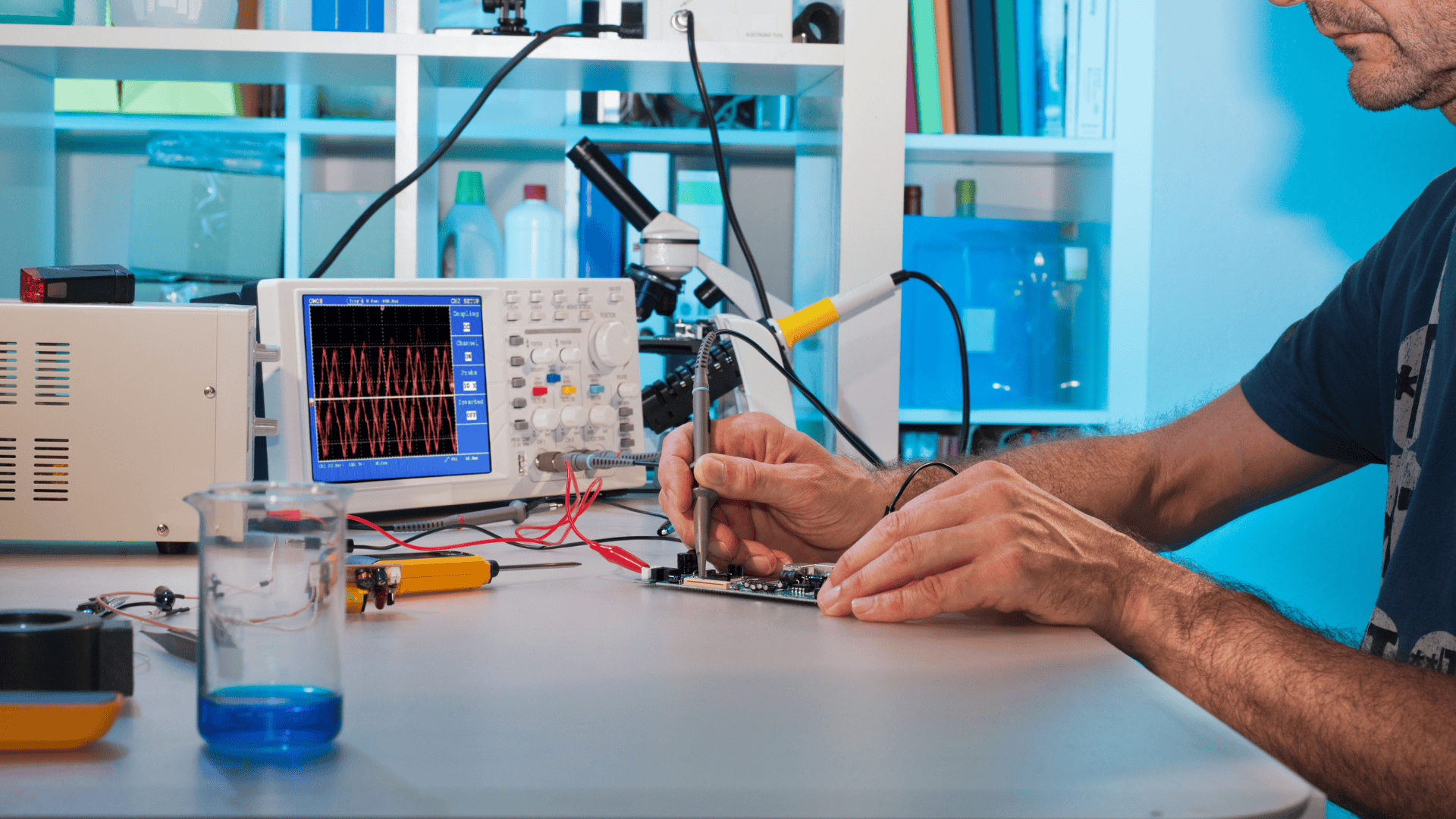
Regulatory compliance is essential for electronics companies to ensure product safety, performance, and environmental responsibility. With varying requirements across regions, staying compliant is key to accessing global markets, avoiding penalties, and earning consumer trust. Navigating these regulations can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be.
In this article, we’ll cover the key regulations you need to know, explore emerging compliance trends, and offer practical advice to help you manage compliance effectively at every stage of product development.
Why is regulatory compliance important for the electronics industry
Regulatory compliance in electronics involves meeting the standards and requirements set by governments, industry bodies, and regulatory agencies to ensure your products are safe, effective, and environmentally responsible. This process typically includes testing, certification, and documentation to verify that products meet specific standards.
Electronics are subject to regulations covering safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), environmental impact, and energy efficiency. Since each region has its regulatory framework, manufacturers face challenges when marketing products internationally.
Key Regulations in Electronics Compliance
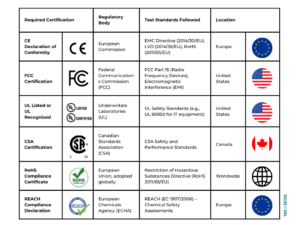
1. CE Marking (Europe)
The CE Mark is required for many products, including electronics, sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). This marking indicates that the product complies with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
To achieve CE marking, products must undergo rigorous testing for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), electrical safety, and compliance with the Low Voltage Directive (LVD).
Key Directives under CE compliance include:
- EMC Directive (2014/30/EU): Ensures that devices do not emit excessive electromagnetic interference and are resistant to external interference.
- Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU): Focuses on electrical safety, covering voltage requirements for products within specific voltage ranges.
- RoHS Directive (2011/65/EU): Restricts the use of hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium in electronics.
Achieving CE marking is critical for market access in Europe, and manufacturers must create a Declaration of Conformity as proof of compliance.
2. FCC Certification (United States)
For products sold in the United States, FCC certification is mandatory for electronic devices that emit radio frequency (RF) energy, including smartphones, computers, and wireless communication devices. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) enforces regulations under Part 15 of its rules, which governs unintentional and intentional radiators.
The key requirements for FCC compliance include:
- FCC Part 15 (Radio Frequency Devices): Governs devices that intentionally emit RF energy, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth devices.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Devices must not interfere with other equipment and must be immune to interference within certain limits.
Manufacturers must test their products in authorized FCC laboratories and submit necessary documentation to obtain FCC certification, which is crucial for accessing the U.S. market.
3. UL Certification (United States)
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is an independent safety certification organization in the United States. UL certification is widely recognized as a mark of product safety and is especially important for electronic devices.
While not mandatory, UL certification is often required by U.S. retailers and consumers, and it demonstrates that a product has been tested for safety hazards.
UL standards cover areas such as:
- Electrical Safety: Ensuring components meet voltage and insulation requirements.
- Fire and Shock Hazards: Preventing risks associated with overheating or electrical faults.
Having UL certification can boost consumer confidence and help meet retailer demands in the U.S. market.
4. CSA Certification (Canada)
For Canadian markets, CSA (Canadian Standards Association) certification is widely recognized. Like UL in the U.S., CSA certification ensures electronic products meet safety and performance standards. CSA-certified products are typically also accepted in the United States.
5. RoHS Compliance (Worldwide)
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) compliance originated in the European Union but has been adopted by countries worldwide. RoHS aims to reduce hazardous substances like lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, and specific flame retardants in electronics, improving environmental and human health.
Key aspects of RoHS include:
- Limiting Hazardous Substances: Ensures that restricted materials do not exceed specified limits.
- Environmental Impact: Reduces pollution and promotes the recycling of electronic products.
RoHS compliance is necessary for entering the European market and is increasingly required globally.
6. REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals)
The REACH regulation, managed by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), focuses on controlling the use of chemicals in products sold within the EU. REACH applies to electronic substances that could be released during use, such as flame retardants or plasticizers.
For compliance, manufacturers must:
- Register Chemicals: Report chemicals used in their products to ECHA.
- Assess Risks: Demonstrate that substances used are safe and do not pose health or environmental hazards.
Compliance with REACH is mandatory for electronics sold in the EU and promotes consumer and environmental protection.
Navigating Regulatory Compliance for Electronics
Bringing an electronic product to market requires meeting various regulatory standards. Here’s how to stay on track and avoid delays:
1. Understand Regional Requirements
Each country, and in some cases, region sets and enforces its compliance regulations, so you must plan for multiple certifications if you intend to sell internationally. To avoid setbacks:
- Research Requirements Early: Identify certification requirements for each market you plan to enter.
- Plan for Multiple Certifications: Factor in regional differences and plan your product development timeline to accommodate the required approvals for each market.
2. Develop a Compliance Checklist Early in the Design Phase
Addressing compliance from the start is essential for preventing costly redesigns and delays:
- Create a Clear Compliance Checklist: Outline all necessary certifications and standards before finalizing your design so you can streamline the development process and ensure all necessary approvals are known and addressed early on before production begins
- Ensure Team Awareness: Make sure engineers and designers follow compliance requirements throughout development.
3. Partner with Accredited Testing Laboratories
Collaborating with recognized testing facilities ensures your product meets regulatory standards for your target market.
- Choose Reliable Labs and agencies: Collaborate with well-equipped accredited test laboratories and with experienced test engineers to streamline the testing and approval process.
- Secure Proper Documentation: Accredited test laboratories are certified to conduct tests and provide the reports needed for clearance for approvals like FCC, UL, or CE.
4. Use Compliance Management System (CMS)
- Track requirements: Monitoring certification deadlines can be overwhelming. Implement CMS for tracking regulatory changes, managing documentation, and streamlining compliance workflows to keep projects on schedule.
- Set Up Alerts and Reminders: Never miss a certification deadline with scheduled reminders for upcoming certifications.
Compliance Trends that may Shape the Electronics Industry

1. Cybersecurity Regulations
As connected devices become more common, governments are enforcing stricter cybersecurity rules to prevent data breaches and hacking. Regulations like the EU Cybersecurity Act and IoT cybersecurity labeling initiatives in the U.S. introduce new compliance requirements that manufacturers must address to ensure secure products.
2. Environmental and Sustainability Standards
Regulators are increasing their focus on sustainability, pushing for eco-friendly design and energy-efficient electronics. Compliance may require meeting eco-design rules, energy efficiency ratings, and recyclability standards. Companies that integrate sustainability into product development meet regulations and align with consumer demand for greener technology.
3. International Standards Harmonization
To facilitate global trade, regulators are working toward unified international standards. Organizations like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) are leading efforts to align compliance requirements across regions, reducing redundant testing and making it easier for manufacturers to sell in multiple markets.
Conclusion
Understanding and navigating regulatory compliance is vital for companies in the electronics sector to ensure market access, product safety, and consumer confidence. By staying informed of the key regulations, incorporating compliance early in design, and leveraging resources like accredited labs and compliance management systems, companies can successfully bring compliant products to market while avoiding costly delays and penalties.