Tackling EMC Compliance Challenges for Brushless DC Motor Projects
August 21, 2024
Table of contents
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) compliance is a critical aspect of designing and developing Brushless DC (BLDC) motors. Ensuring that BLDC motor projects meet EMC standards is essential not only for preventing electromagnetic interference (EMI) but also for guaranteeing the safe and reliable operation of electronic devices in various environments.
Without proper EMC compliance, BLDC motors could disrupt other nearby electronic systems, leading to malfunctions, performance degradation, or even failures in critical applications. Achieving EMC compliance requires a thorough understanding of regulations, precise design, rigorous testing, and careful selection of components. This makes EMC a key factor in the successful deployment of BLDC motors in industries such as automotive, robotics, and industrial automation.
What is EMC?
EMC refers to the ability of electrical equipment to function satisfactorily in its electromagnetic environment without introducing intolerable electromagnetic disturbances to anything in that environment.
For BLDC motors, this means minimizing EMI that can affect the motor’s performance or other electronic systems in proximity. In this article, we will explore the common EMC compliance challenges faced in BLDC motor projects and provide detailed insights into overcoming these challenges.
Identifying Sources of EMI in BLDC Motors
Switching Noise
BLDC motors operate using electronic commutation, which involves rapidly switching currents in the motor windings. This switching can generate high-frequency noise, a significant source of EMI. Managing switching noise is crucial for EMC compliance.
Power Supply Noise
The power supply for BLDC motors can introduce noise into the system. Voltage spikes and transients from the power supply can couple into the motor’s circuitry, creating EMI issues. Ensuring a clean power supply is vital.
Grounding and Shielding Issues
Improper grounding and shielding can exacerbate EMI problems. Effective grounding and shielding techniques are essential to minimize radiated and conducted emissions from BLDC motors.
Mitigating EMI in BLDC Motor Projects
Implementing Proper Filtering Techniques
Filters are critical components in reducing EMI. Using capacitors and inductors to filter high-frequency noise can significantly mitigate EMI. Common filter types include:
- Low-pass filters: Allow low-frequency signals to pass while attenuating high-frequency noise.
- Common-mode chokes: Reduce common-mode noise on power and signal lines.
Designing Effective PCB Layouts
The layout of the printed circuit board (PCB) plays a crucial role in minimizing EMI. Key considerations for PCB design include:
- Shortening trace lengths: Reduce the antenna effect that can radiate EMI.
- Separating power and signal traces: Minimize coupling of noise between power and signal lines.
- Using ground planes: Provide a low-impedance path for return currents, reducing radiated emissions.
Proper Grounding and Shielding
Effective grounding and shielding techniques are essential for reducing EMI. Strategies include:
- Star grounding: Connect all grounds to a single point to avoid ground loops.
- Shielded cables: Use shielded cables for signal and power lines to prevent radiated EMI.
- Enclosures: Use metal enclosures to shield sensitive components from external EMI.
Testing for EMC Compliance
Pre-Compliance Testing
Conducting pre-compliance testing during the development phase helps identify and address EMI issues early. Common pre-compliance tests include:
- Radiated emissions testing: Measure the electromagnetic radiation emitted from the BLDC motor.
- Conducted emissions testing: Assess the noise conducted back onto the power lines.
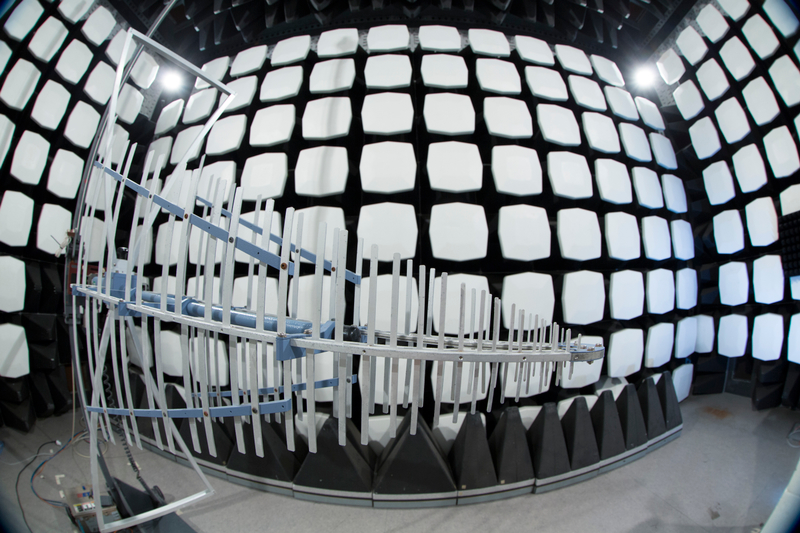
Using EMC Test Chambers
EMC test chambers provide a controlled environment for accurate EMI measurements, which is essential for identifying EMI sources and testing mitigation strategies.
Compliance with Standards
Ensure that your BLDC motor project meets relevant EMC standards, such as:
- CISPR 25: Specifies limits for radiated and conducted emissions in vehicles.
- EN 55032: Defines limits for multimedia equipment emissions.
- IEC 61000-6-3: General emission standard for residential, commercial, and light-industrial environments.
Addressing Specific EMC Challenges in BLDC Motors
High-Speed Operation
High-speed operation of BLDC motors can generate more significant EMI due to higher switching frequencies. To address this challenge:
- Optimize switching frequencies: Choose frequencies that minimize EMI without compromising performance.
- Use spread spectrum techniques: Distribute the energy of the EMI over a wider frequency range, reducing peak emissions.
Integration with Other Electronic Systems
Integrating BLDC motors with other electronic systems can introduce additional EMI challenges. To mitigate these issues:
- Isolate sensitive components: Physically separate the BLDC motor from sensitive electronic components.
- Use differential signaling: Reduce susceptibility to EMI by using differential pairs for signal transmission.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, can affect EMI performance. Consider the following:
- Temperature compensation: Ensure components are rated for the operating temperature range to maintain EMI performance.
- Moisture protection: Use conformal coatings to protect against moisture-induced EMI issues.
Practical Tips for Ensuring EMC Compliance
Collaborative Design Approach
Taking a collaborative design approach is essential for ensuring electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) in brushless DC (BLDC) motor projects. By involving EMC experts early in the design phase, you can proactively identify potential sources of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and address them before they become significant issues.
EMC experts bring specialized knowledge that can guide design decisions, such as optimal circuit layout, component selection, and noise mitigation strategies. This collaboration allows for the implementation of effective EMI suppression techniques, such as shielding, filtering, and grounding, right from the
start. A team-based approach helps ensure that all aspects of the design are aligned with EMC standards, ultimately saving time and reducing costly redesigns later.
Continuous Monitoring and Testing
Continuous monitoring and testing for EMI throughout the development process are vital for maintaining EMC compliance. Regular testing helps catch EMI issues early, enabling engineers to make timely adjustments and prevent problems from escalating as the project progresses.
This ongoing testing should be integrated into every stage of development, from initial prototypes to final production. Utilizing tools such as spectrum analyzers, oscilloscopes, and specialized EMC testing equipment can help identify and measure EMI levels in real time.
Early detection of EMI issues allows for quicker resolution, ensuring that the final product meets EMC standards and performs reliably in its intended environment.
Documentation and Compliance Reports
Thorough documentation of your EMC design practices and test results is crucial for ensuring compliance and facilitating future troubleshooting.
Detailed records of all design decisions, testing methodologies, and corrective actions provide a clear audit trail, which is invaluable when seeking EMC certification.
Compliance reports, which summarize test results and demonstrate adherence to relevant standards, are essential for certification processes in various markets, including the EU, where CE marking is required.
Additionally, maintaining comprehensive documentation can streamline future product iterations, as it provides a reference point for addressing any EMI issues that may arise post-production. These records also help in demonstrating due diligence and regulatory compliance to clients, certification bodies, and other stakeholders.
Conclusion
Achieving EMC compliance in BLDC motor projects requires a thorough understanding of EMI sources and effective mitigation strategies.
By implementing proper filtering, grounding, shielding, and testing techniques, you can ensure that your BLDC motors meet EMC standards and perform reliably in their intended applications.
Addressing EMC challenges early in the design process will save time and resources, leading to a smoother path to market readiness.